High voltage switchgear operates at voltages above 36 kV and is essential for efficient power distribution and protection. It interrupts electrical currents via components such as circuit breakers, disconnectors, and earthing switches. These elements work to isolate faults, maintain system stability, and guarantee safety. The various types, including GIS and AIS, offer different benefits based on the application. For those looking to explore further, the intricacies of these systems offer an insightful perspective on modern electrical infrastructure.
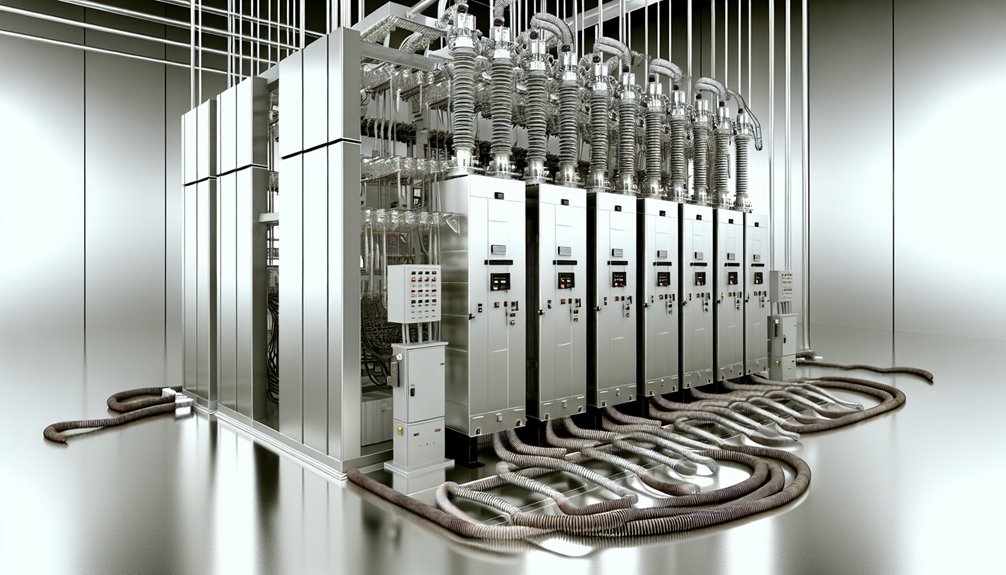

High voltage switchgear, operating at voltages exceeding 36 kV, is essential to the protection and efficient functioning of high voltage power systems. This critical infrastructure guarantees uninterrupted power supply by automatically isolating malfunctioning equipment to prevent abnormal current buildups.
The components of high voltage switchgear, such as circuit breakers, isolators, and relays, work cohesively to control, protect, and isolate electrical circuits. The high voltage switchgear working principle involves switching electrical currents on and off, safeguarding equipment from overloads and short circuits, and maintaining system integrity.
This secures safe operation by quickly interrupting current flow during faults, preventing equipment damage, and protecting personnel. The precise coordination of these components is crucial for maintaining robust power network operations.
Operating at voltages exceeding 36 kV, high voltage switchgear systems play a fundamental role in the protection and efficiency of power systems.
These systems guarantee the seamless operation and safety of electrical networks by executing critical functions guided by IEC 62271 high voltage switchgear standards.
Key functions include:
These functions collectively guarantee the high voltage switchgear's pivotal role in modern power infrastructure.
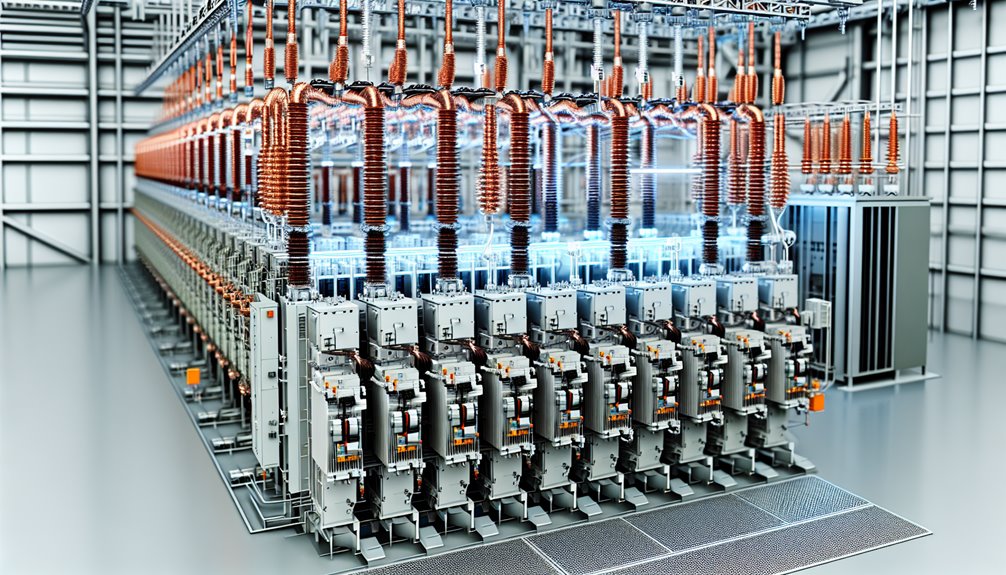
High voltage switchgear operates by controlling, protecting, and monitoring electrical power systems through a combination of sophisticated components and processes.
The operating principle involves the interruption of current and extinguishing of arcs, primarily achieved using circuit breakers and advanced arc-quenching methods.
Additionally, monitoring and relay systems, coupled with automation, guarantee efficient operation, fault detection, and system reliability in high voltage environments.
The operational principle of high voltage switchgear revolves around its ability to manage the flow of electrical energy within power systems. This management is achieved through precise switching and isolation of electrical circuits. High voltage switchgear, including air insulated switchgear (AIS) and gas insulated switchgear (GIS), functions to control and protect these circuits while ensuring system stability.
Through these mechanisms, high voltage switchgear plays a critical role in the reliability and efficiency of power systems.
When high voltage switchgear is engaged in the interruption of current, it initiates a sophisticated process that mitigates the risks associated with electrical faults. This process involves the rapid separation of circuit contacts, creating an electric arc.
To extinguish this arc, high voltage switchgear employs various mechanisms aligned with arc flash protection standards. Gas insulated switchgear (GIS), for instance, utilizes SF6 gas to effectively cool and quench the arc, guaranteeing safe interruption.
The precision of this operation is critical, as it prevents equipment damage and guarantees personnel safety. Through these advanced techniques, high voltage switchgear maintains system stability, controlling the flow of electrical energy while minimizing the potential for hazardous incidents in high voltage environments.
Although high voltage systems operate at significant power levels, effective monitoring, relays, and automation are essential for maintaining their operational integrity and safety. High voltage switchgear, whether air insulated switchgear (AIS) or gas insulated switchgear (GIS), relies on sophisticated systems to guarantee seamless performance.
These components collectively guarantee that high voltage switchgear systems remain efficient, secure, and operational under various conditions, providing control to operators.
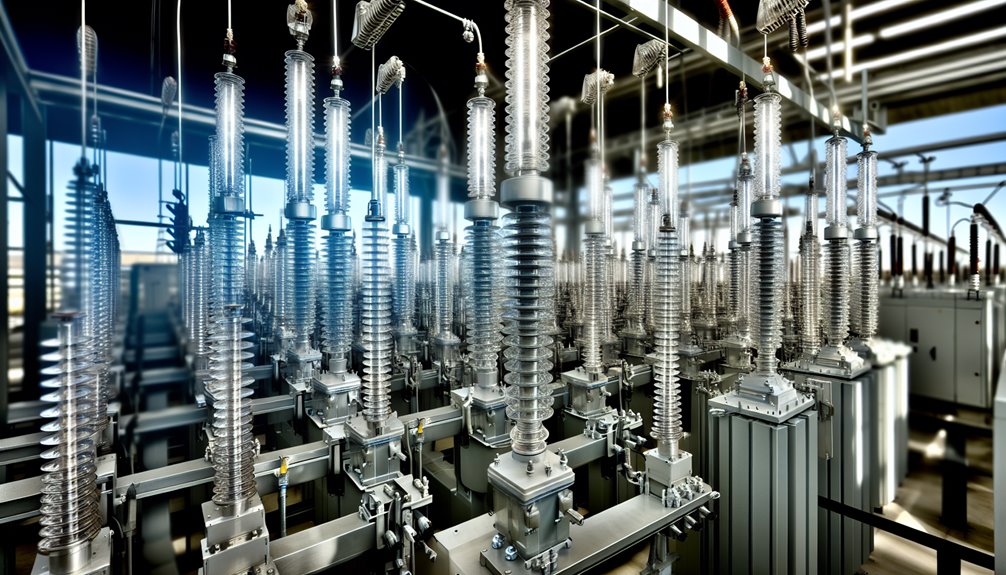

High voltage switchgear is comprised of several critical components, each serving a distinct role in ensuring the safety and functionality of power systems.
Circuit breakers, disconnectors, and earthing switches work collectively to manage and isolate electrical circuits, preventing overloads and maintaining system integrity.
Additionally, instrument transformers, relays, busbars, surge arresters, control panels, and auxiliary systems provide essential monitoring, protection, and control functions, thereby enhancing the overall reliability and efficiency of high voltage infrastructure.
Circuit breakers serve as critical components in high voltage switchgear, designed to interrupt the flow of electrical current during fault conditions. These devices enhance system reliability by protecting circuits from overloads and short circuits.
High voltage switchgear benefits considerably from advanced circuit breaker technology, which has improved reliability over the last 15 years.
To guarantee peak performance and longevity, a maintenance guide is essential for addressing potential issues such as:
These measures support effective fault management and system safety.
Disconnectors and earthing switches are fundamental components in high voltage switchgear, serving essential roles in the safe operation and maintenance of electrical systems.
Disconnecting switches are designed to mechanically isolate circuits, ensuring that maintenance and repairs can be conducted without the risk of electrical hazards. By providing a visible break in the circuit, disconnectors offer a clear indication of isolation, thereby enhancing safety protocols.
Meanwhile, earthing switches establish a secure ground connection to dissipate electrical charges safely, preventing potential faults and ensuring personnel safety during maintenance activities.
Both components are integral to the reliable functioning of high voltage switchgear, offering critical protection and operational control that aligns with the stringent demands of high voltage environments, thereby underpinning system integrity and safety.
Instrument transformers and relays form the backbone of high voltage switchgear systems, ensuring accurate measurement and protection functions.
Instrument transformers reduce high current and voltage levels to a manageable range for monitoring and control. This is essential for precise system operation and fault detection.
Relays, on the other hand, automate response mechanisms, safeguarding the integrity of the electrical network. They are vital in executing protection functions, such as:
Together, these components enhance the reliability and safety of high voltage switchgear systems.
Busbars and surge arresters are essential components of high voltage switchgear, playing a significant role in guaranteeing efficient power distribution and system protection.
In high voltage switchgear, busbars facilitate the distribution of electrical power by providing a common connection point for multiple circuits, guaranteeing minimal energy loss and reliable performance. These components are integral to both air insulated switchgear (AIS) and gas insulated switchgear (GIS), where they accommodate varying voltage levels and environmental conditions.
Surge arresters protect the system from transients caused by lightning strikes or switching operations, preventing potential damage to sensitive equipment. By maintaining system integrity, these components guarantee operational safety and efficiency, critical for the stability of modern electrical networks operating above 36 kV.
Control panels and auxiliary systems are foundational components of high voltage switchgear, meticulously designed to confirm precise management and monitoring of electrical circuits. The integration of these systems confirms operational efficiency and safety across diverse switchgear types, such as air insulated switchgear (AIS) and gas insulated switchgear (GIS).
Key functions include:
Such components are indispensable for maintaining the integrity and performance of high voltage power systems.
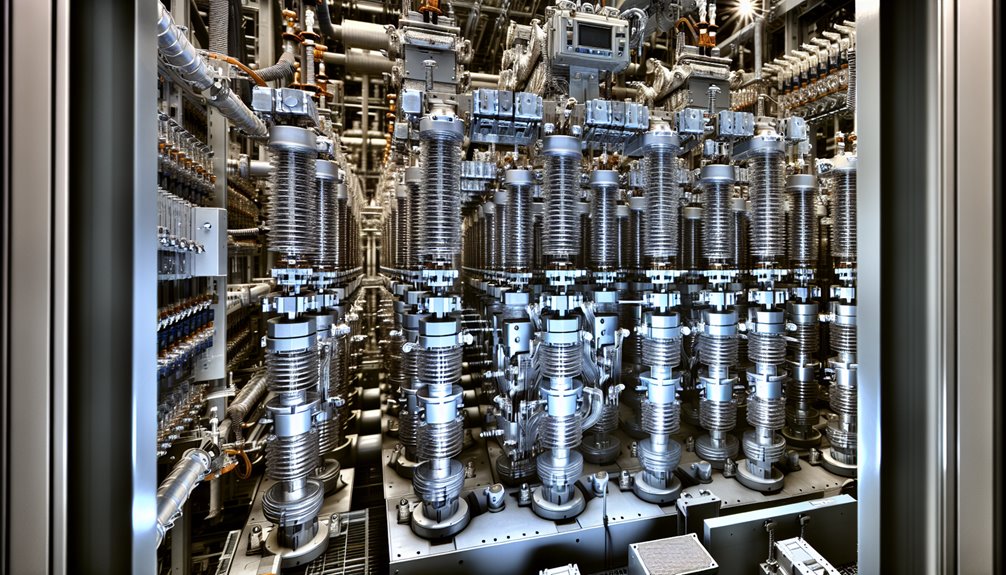
High voltage switchgear can be categorized based on insulation type, with key variants including Air-Insulated Switchgear (AIS) and Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS), each offering distinct advantages and limitations.
Additional options such as Hybrid, Solid-Insulated, and Oil-Insulated Switchgear provide tailored solutions for specific operational environments.
These types are selected primarily based on considerations of cost, space constraints, and environmental impact, ensuring ideal performance and safety in various applications.
Air-Insulated Switchgear (AIS) represents a traditional and practical choice for high voltage power systems, particularly in outdoor settings where space constraints are not a primary concern.
AIS is favored for its lower initial cost and ease of maintenance, as highlighted in high voltage switchgear maintenance guides. However, it requires more space and is susceptible to environmental factors.
Key characteristics include:
AIS remains a viable option where spatial resources are abundant.
Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS) represents a significant advancement in the design and functionality of high voltage switchgear, particularly suited for environments where space is limited.
GIS utilizes SF6 gas for insulation, enabling a compact, reliable configuration that excels in urban settings and industrial plants. Unlike Air-Insulated Switchgear (AIS), GIS is less influenced by environmental factors such as pollution.
However, it requires specialized knowledge for maintaining the SF6 gas, which poses environmental concerns, prompting the development of SF6-free switchgear technology.
The high reliability and enhanced safety of GIS make it an excellent choice for indoor substations with limited space.
Despite its higher initial cost compared to AIS, its benefits in space efficiency and reliability justify its investment in space-constrained applications.
Building upon the functionalities of Gas-Insulated Switchgear (GIS), hybrid switchgear introduces a versatile solution that combines the strengths of both air and gas insulation technologies.
This innovative approach offers a balanced performance profile with several distinct advantages that cater to diverse electrical infrastructure requirements.
Solid-insulated switchgear represents an innovative solution within the realm of high voltage equipment, offering a distinct alternative to traditional insulation methods. This type of switchgear eschews the use of SF6 gas, making it environmentally friendly.
However, it may not match the robustness of gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) or the cost-effectiveness of air-insulated switchgear (AIS). Solid insulation materials, typically epoxy resin, provide adequate dielectric strength and can be used in compact configurations suitable for indoor use.
This makes them ideal for applications where environmental impact is a priority and space is limited. Despite its advantages, users must consider trade-offs regarding reliability and initial investment compared to other types of switchgear.
Therefore, solid-insulated switchgear is a strategic choice for eco-conscious installations.
Following the exploration of solid-insulated switchgear, oil-insulated switchgear emerges as another remarkable variant in high voltage applications. This type leverages mineral oil as its primary insulation medium, offering several advantages and drawbacks.
Vacuum switchgear stands out as a pivotal component in high voltage electrical systems, employing vacuum interrupters for efficient circuit breaking. This type of switchgear is recognized for its high dielectric strength and reliability, ensuring effective interruption of electrical currents.
The vacuum interrupter operates by extinguishing arcs in a vacuum environment, thereby minimizing the risk of arc re-ignition. Its compact design allows for installation in restricted spaces, aligning with modern infrastructure demands.
However, vacuum switchgear is mainly suitable for medium to high voltage applications and may not accommodate the highest voltage ranges. Despite this limitation, its low maintenance requirements and robust performance make it a preferred choice in applications where reliability and space efficiency are paramount.
High voltage switchgear incorporates critical protection and safety functions, essential for maintaining system integrity and personnel safety.
These systems are designed with advanced fault detection and isolation mechanisms, overcurrent and short-circuit protection, and arc-flash resistance, all adhering to international standards such as IEC 62271, ANSI/IEEE, and NFPA 70E.
Compliance with these standards guarantees that switchgear effectively mitigates electrical hazards while optimizing operational reliability.
Fault detection and isolation are critical functions within high voltage switchgear systems, serving as the cornerstone for protection and safety in electrical networks. By identifying and isolating faults, the system guarantees continuity of service while safeguarding equipment and personnel.
Effective fault detection and isolation involve the integration of sophisticated technologies and precise execution. Key elements include:
Incorporating these components enhances the reliability and efficiency of high voltage systems, mitigating the risk of widespread disruptions.
While guaranteeing the safety and reliability of electrical systems, overcurrent and short-circuit protection are essential functions implemented in high voltage switchgear. These mechanisms are designed to detect abnormal current flows, such as those exceeding the normal operating limits or caused by short circuits.
Circuit breakers and relays serve as critical components, promptly interrupting current flow to protect both equipment and personnel from potential damage or hazards. The precision of these devices is vital, as delays in response can lead to catastrophic failures or extended downtime.
Arc-flash resistance represents a critical aspect of electrical safety in high voltage switchgear systems. It involves measures to prevent and mitigate the effects of arc-flash incidents, which pose severe risks to personnel and equipment.
Key components of arc-flash resistance include:
Implementing robust arc-flash resistance measures in high voltage switchgear guarantees enhanced safety and operational reliability, safeguarding both human lives and infrastructure.
Compliance with IEC 62271, ANSI/IEEE, and NFPA 70E standards is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of high voltage switchgear systems.
These standards provide thorough guidelines for design, testing, and operation, minimizing risks associated with electrical hazards. IEC 62271 specifies the requirements for high voltage switchgear, focusing on performance and safety under varied conditions.
ANSI/IEEE standards address electrical system performance and safety, ensuring consistent operating conditions across different installations. NFPA 70E emphasizes workplace safety, outlining strategies to mitigate arc-flash hazards.
Adherence to these standards helps in achieving peak system performance, enhancing protection for personnel and equipment. Consequently, the integration of these guidelines into switchgear design and operation is fundamental to maintaining a secure and efficient power distribution network.
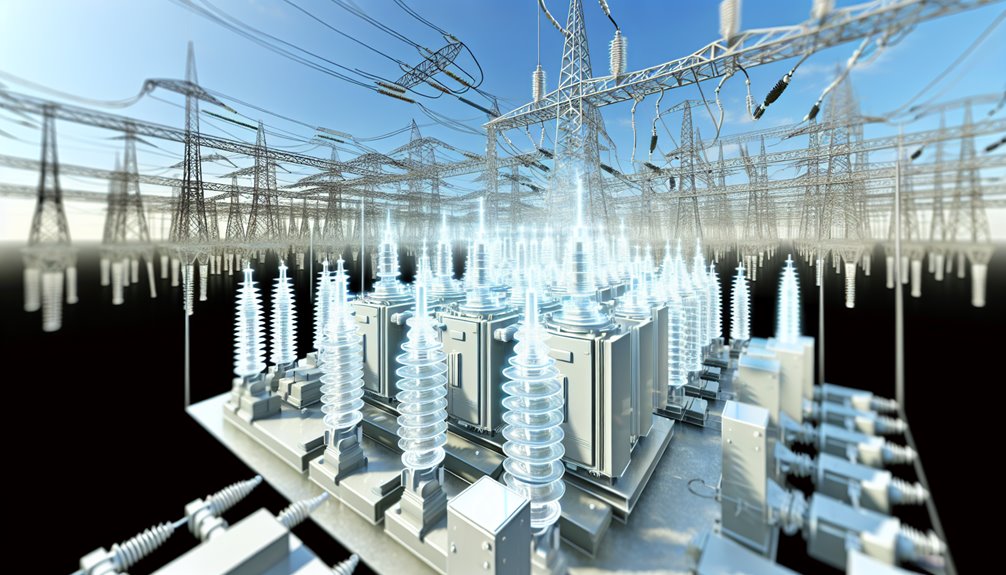

High voltage switchgear plays a critical role in ensuring the efficient operation and safety of power generation and transmission systems by facilitating reliable connections and disconnections of generators and managing voltage levels across substations.
In industrial and mining operations, it supports the management of power to heavy machinery and processes, while in renewable energy integration, it aids in connecting solar farms and wind turbines to the grid, handling their variable outputs.
Additionally, high voltage switchgear is essential for maintaining power stability in infrastructure projects and data centers, where uninterrupted supply is vital for operational continuity.
In the domain of electrical power systems, high voltage switchgear plays a pivotal role in the efficient operation of power generation and transmission. It is indispensable in managing and protecting electrical infrastructure, ensuring stability and continuity of service.
Among its significant applications:
Through these applications, high voltage switchgear enhances system reliability and optimizes power flow across networks.
Many industrial and mining operations rely heavily on high voltage switchgear for their power management needs, a critical component that guarantees operational efficiency and safety.
High voltage switchgear is indispensable in controlling and protecting the electrical equipment that powers large machinery and processes within these sectors. By isolating faults and maintaining uninterrupted power supply, it supports critical operations, minimizing downtime and preserving system integrity.
The integration of circuit breakers, relays, and transformers within the switchgear facilitates precise management of power distribution, accommodating the high demand typical of mining and industrial environments.
Moreover, its robust design guarantees resilience against harsh conditions, a common challenge in these sectors, thereby upholding safety standards and optimizing energy use.
The deployment of high voltage switchgear plays a pivotal role in renewable energy integration by efficiently managing the complexities associated with variable power outputs from renewable sources.
This technology guarantees the stable operation of solar farms and wind turbines, which are inherently intermittent. High voltage switchgear facilitates the seamless connection of these renewable sources to the grid, enabling optimized power flow and system reliability.
Key applications include:
Infrastructure and data centers represent a vital domain for high voltage switchgear applications, given their need for robust power management solutions.
In large commercial buildings, such as shopping malls and data centers, high voltage switchgear guarantees a reliable power supply to critical systems, minimizing risk of downtime. The switchgear's ability to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment is indispensable for maintaining the stability and efficiency of power systems within these facilities.
It facilitates seamless power distribution and fault management, essential for the uninterrupted operation of sensitive data processing equipment. Additionally, its application in industrial plants supports the management of power to large machinery, guaranteeing operational continuity and safety in manufacturing and processing environments.
High voltage switchgear, consequently, underpins the robust infrastructure vital for modern industrial and commercial operations.
Routine inspection and testing of high voltage switchgear are critical procedures to guarantee peak performance and longevity.
Common issues such as internal noise and overheated connectors can arise, necessitating precise troubleshooting techniques to identify and mitigate these problems effectively.
Regular maintenance and timely resolution of faults are essential to maintain system reliability and prevent operational disruptions.
Conducting regular inspections and testing is vital for maintaining the reliability and safety of high voltage switchgear systems. Inspections encompass visual checks and basic operational assessments, ensuring all components are in ideal condition without dismantling. By adhering to a structured inspection and servicing schedule, potential issues can be identified and addressed promptly.
High voltage switchgear systems often encounter issues such as overheating and loose connections, ground faults, and insulation failures, which can compromise their operational integrity.
Mechanical interlock problems further complicate maintenance efforts, necessitating a careful balance between preventive and corrective maintenance strategies to mitigate potential risks.
Addressing these challenges requires a systematic approach to diagnostics and the implementation of robust maintenance protocols to guarantee reliability and safety in power systems.
Overheating and loose connections are prevalent issues in the maintenance and troubleshooting of high voltage (HV) switchgear, impacting both performance and safety.
Technicians must address these concerns by implementing strict maintenance protocols:
Addressing common issues such as overheating and loose connections provides a foundation for understanding other critical concerns in high voltage switchgear maintenance, including ground faults and insulation failures.
Ground faults arise from unintended conductive paths, risking equipment damage. Insulation failures, often due to aging or environmental factors, compromise system integrity.
Routine inspections and non-destructive testing are imperative in identifying these issues and preventing operational disruptions.
Mechanical interlock problems in high voltage switchgear are critical issues that can greatly impact the safety and functionality of electrical systems.
These issues often arise due to misalignment or wear of mechanical components, leading to operational failures.
Key troubleshooting steps include:
Effective maintenance strategies are imperative for ensuring the operational reliability and safety of high-voltage switchgear systems. Preventive maintenance involves regular inspections and servicing to avert failures, while corrective maintenance addresses issues post-failure. The choice between the two depends on factors like cost, downtime, and risk management.
| Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Preventive | Reduces risk of unexpected equipment failure through regular inspections and servicing | Higher initial maintenance and scheduling cost |
| Corrective | Lower upfront investment; maintenance performed only after issues arise | Increased risk of unplanned downtime and potential damage |
| Combination | Offers a balanced approach with preventive actions for critical components and corrective responses for minor issues | Requires careful planning and resource management |

Amid the growing complexities of modern power systems, innovations in high voltage switchgear are poised to transform the energy landscape through advanced technology and sustainable practices.
High-voltage research and development (R&D) is focused on several key areas:
These innovations highlight the critical role of R&D in advancing high-voltage switchgear technology.
Guaranteeing safety in high voltage switchgear operations necessitates rigorous adherence to best practices and extensive operator training. Operators must be proficient in recognizing and mitigating potential hazards, including electrical shock, arc flash, and equipment failure.
Thorough training programs should cover the operation, maintenance, and emergency protocols specific to high voltage systems. Personal protective equipment is mandatory, including insulating gloves, arc-rated clothing, and face shields.
Regular safety audits and drills are imperative to reinforce protocols and assess readiness. Detailed procedural documentation should guide operations, emphasizing lockout/tagout procedures and verification of de-energization.
Continuous education and certification guarantee operators remain updated on technological advancements and regulatory changes, fostering a culture of safety and operational excellence within high voltage environments.
[SUBHEADING IMAGE SLOT 38]
Switchgear, integral to electrical systems, is categorized into low, medium, and high voltage types, each serving distinct roles based on voltage levels and applications.
These categories guarantee tailored solutions for diverse electrical needs and safety standards.
It includes circuit breakers, fuses, and isolators, providing cost-effective and straightforward installation.
It offers a balance of performance and cost, featuring gas-insulated units and protective relays.
It guarantees the management of high energy with components like SF6 circuit breakers and advanced arcing protection.
At Conya Electric, we take pride in our legacy of over three decades in the power distribution industry. Founded in 1988 as Foshan Xinya Switch Factory, we have grown into a trusted global brand recognised for our commitment to innovation, precision engineering, and uncompromising quality.
With ISO-certified quality management systems and CCC product certifications, we ensure every product meets the highest safety and performance standards. Our long-standing collaborations with global leaders such as ABB, Eaton, and AEG enable us to integrate advanced technologies and deliver comprehensive, value-driven solutions to our clients worldwide.
| Certification Type | Industry Collaboration | Customer Focus |
|---|---|---|
| ISO Quality System | ABB, Eaton, AEG | Customised equipment solutions |
| CCC Product Certification | Authorized Distribution Factory | End-to-end project support |
| Strategic Partnerships | Leading Global Electrical Brands | Technical consultation and after-sales service |
We serve a broad range of industries — including rail transit, photovoltaic energy storage, industrial automation, and intelligent power systems — providing custom-engineered, professional solutions that ensure safety, efficiency, and long-term reliability.
👉 Partner with Conya Electric to experience engineering excellence, personalised service, and reliable power distribution solutions that keep your operations running smoothly.
Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements or OEM partnership opportunities.
SF6 gas in high voltage switchgear poses significant environmental concerns due to its potent greenhouse effect, having a global warming potential approximately 23,500 times greater than CO2, necessitating stringent handling, recycling, and leakage prevention measures to mitigate impact.
High voltage switchgear integrates into renewable energy systems by managing and protecting high-voltage transmission from renewable sources, ensuring efficient power distribution, minimizing faults, and maintaining stability through advanced control, monitoring, and fault detection technologies essential for grid reliability.
Manufacturing high voltage switchgear requires certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and IEC 62271 for high voltage standards. Compliance guarantees safety, reliability, and adherence to international standards in production processes.
High voltage switchgear enhances grid stability by efficiently managing power flow and isolating faults, reducing outage risks. It enables over 99% fault clearance rate, essential for maintaining uninterrupted electricity supply and protecting infrastructure from damage.
Cost considerations for installing high voltage switchgear include initial equipment cost, installation, maintenance, and operational expenses. Factors like system complexity, site-specific requirements, and future scalability impact total expenditure, necessitating thorough financial planning for sustainable and efficient deployment.